Cloud adoption is rising at rocket speed. Organizations are shifting to AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to gain scale, performance, and flexibility. But with rapid cloud transformation comes a harsh truth:
Misconfigurations are the #1 cause of cloud security incidents.
Studies show that over 80% of cloud breaches originate from simple configuration mistakes—public S3 buckets, overly permissive IAM roles, exposed databases, unsecured VM ports, and more.
Traditional security methods simply cannot keep up with the pace of cloud change.
Teams deploy daily, resources scale automatically, and settings shift constantly.
This is where Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) steps in.
CSPM brings automation, visibility, and continuous monitoring—helping teams detect weaknesses before attackers do. Let’s break it down in a clear and practical way.
Understanding Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Defining CSPM: The Core Concept
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) refers to tools that analyze cloud configurations, detect misconfigurations, enforce security policies, and ensure compliance across environments like AWS, Azure, and GCP.
In simple terms:
👉 CSPM is your 24/7 cloud security guard.
It continuously checks:
- Identity & access rules
- Storage permissions
- Network exposure
- Encryption settings
- Audit logs
- Resource policies
If anything drifts from best practices, CSPM flags it—or even auto-fixes it.
Without CSPM, blind spots explode as cloud complexity grows.
How CSPM Differs from Traditional Security Tools
Traditional security tools focus on apps and networks.
- Vulnerability scanners → find code weaknesses
- SIEM → collects logs and alerts on suspicious activity
- Firewalls → stop network-based attacks
CSPM is different. It focuses on cloud configurations.
It inspects the control plane, not the application layer.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
| Feature | CSPM | Traditional Security |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Cloud configs & policies | Code vulnerabilities & network threats |
| Scope | Entire cloud environment | Apps, hosts, network |
| Approach | Agentless API-based scanning | Log-based or agent-based |
| Outcome | Prevents breaches via misconfig detection | Reacts after alerts |
Why this matters:
A single misconfigured S3 bucket can expose millions of records—even if your app is secure. Traditional tools won’t catch that. CSPM will.
Key Capabilities of a CSPM Solution
Modern CSPM solutions bring powerful features, including:
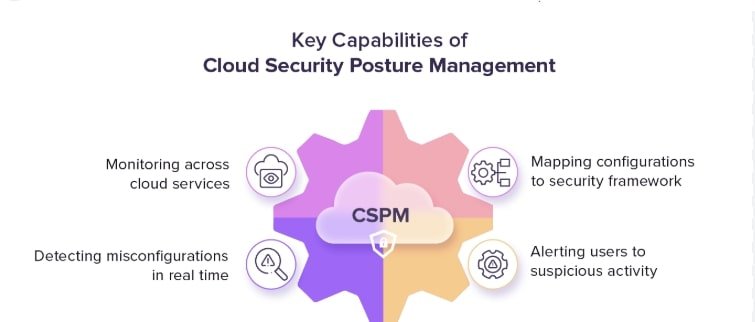
Continuous cloud scanning via API
Detect risks instantly—no agents needed.
Misconfiguration detection
Examples include:
- Publicly exposed databases
- Overly permissive IAM roles
- Unguarded ports (like 0.0.0.0/0 on SSH)
- Unencrypted storage volumes
Risk scoring & prioritization
Critical issues rise to the top so teams fix what matters first.
Automated remediation
Some CSPMs can auto-correct dangerous changes—within seconds.
Policy enforcement
You define standards once; CSPM enforces them across all accounts and clouds.
Compliance monitoring
Supports CIS Benchmarks, NIST, PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, ISO 27001, etc.
Why CSPM Is Critical in Modern Cloud Operations

1. Preventing Data Breaches Caused by Configuration Drift
Cloud environments change constantly. Developers scale resources, add permissions, and tweak configs—often without security oversight.
This leads to configuration drift, one of the biggest cloud risks.
Example: The 2019 Capital One breach
A simple AWS IAM misconfiguration allowed access to sensitive data of 100M+ customers.
A CSPM tool would have spotted the misconfig long before it was exploited.
CSPM prevents:
- Public storage exposure
- Excessive permissions
- Unrestricted network access
- Data leakage through misconfigured backups
In fast-moving DevOps environments, CSPM becomes essential to avoid breach-level mistakes.
2. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance and Audit Readiness
Industries governed by GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, PCI DSS, and other frameworks require strict controls. Manually checking compliance in AWS or Azure is painful and error-prone.
CSPM solves this with:
- Real-time compliance scoring
- Automated checklists
- Prebuilt benchmark templates
- Auto-generated audit reports
This means teams can prove compliance in minutes—not weeks.
As experts say:
Manual compliance checks fail in dynamic clouds. CSPM delivers continuous proof.
3. Managing Multi-Cloud Complexity
Today’s enterprises run multi-cloud by default:
AWS for compute, Azure for enterprise services, GCP for analytics.
Each cloud has unique security models:
- AWS IAM
- Azure RBAC
- GCP IAM and permissions
This creates fragmentation, blind spots, and inconsistent controls.
CSPM fixes that by:
- Unifying visibility
- Standardizing policies
- Detecting inconsistencies
- Offering a single security dashboard
In multi-cloud environments, CSPM becomes the centralized command center for security.
How CSPM Works: The Core Mechanics
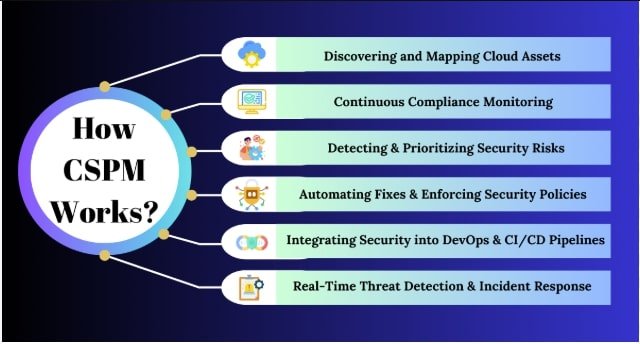
1. Continuous Discovery & Asset Inventory
CSPM connects to your cloud through read-only APIs and discovers:
- VMs
- Databases
- Storage buckets
- Containers
- Serverless functions
- Network paths
- IAM entities
This creates a live inventory of your entire cloud environment.
2. Policy Benchmarking
Using frameworks like CIS Benchmarks, NIST, SOC 2, or custom rules, CSPM checks:
- Identity policies
- Encryption settings
- Network rules
- Storage exposure
- Logging and monitoring configurations
3. Risk Prioritization & Contextual Remediation
CSPM analyzes:
- Severity
- Exploitability
- Data sensitivity
- Business impact
…and gives clear remediation steps (sometimes automated).
Agentless scanning makes this fast, scalable, and maintenance-free.
CSPM Integration and Future Trends
Shift-Left Security: Integrating CSPM Into CI/CD Pipelines
Modern DevOps pipelines rely on Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) such as Terraform, CloudFormation, or ARM templates.
CSPM tools now scan IaC before deployment, catching misconfigs early.
This prevents insecure infrastructure from ever going live.
The Convergence of CSPM, CWPP, and CNAPP
The future of cloud security is CNAPP (Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform).
CNAPP merges:
- CSPM → configuration security
- CWPP → workload security
- CIEM → identity & access governance
- IaC scanning → shift-left checks
This creates full lifecycle protection:
code → cloud → runtime.
Automation & Auto-Remediation
Modern CSPM platforms offer:
- Auto-correcting open ports
- Reverting insecure IAM policies
- Enforcing encryption
- Blocking resource exposure
This reduces Mean Time To Remediate (MTTR) from days to minutes.
Governance rules can control which fixes are automated vs manual.
Conclusion: CSPM is the Foundation of Cloud-Native Security
In today’s cloud-first world, CSPM is no longer optional—it’s essential.
Key takeaways:
- CSPM prevents misconfig-related breaches—the biggest cloud threat today.
- It ensures compliance across multiple regulatory standards.
- It unifies multi-cloud security into a single pane of glass.
- It automates remediation and reduces human error.
- It integrates with DevOps to stop misconfigs from ever reaching production.
As cloud environments grow more dynamic and complex, CSPM delivers the visibility and control that manual processes cannot.
If you want a secure, resilient cloud environment—CSPM is the place to start.
FAQs About Mastering Cloud Security
1️⃣ What is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) in simple terms?
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is a security solution that continuously monitors cloud environments like AWS, Azure, and GCP to detect and fix misconfigurations.
It works through API-based scanning and ensures that cloud resources follow security best practices and compliance standards such as CIS, NIST, and ISO 27001.
In short, CSPM prevents cloud breaches caused by configuration mistakes before attackers can exploit them.
2️⃣ Why is CSPM important for AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud?
CSPM is critical because most cloud breaches happen due to misconfigurations—like public S3 buckets, exposed databases, or overly permissive IAM roles.
Traditional security tools don’t monitor cloud control plane configurations. CSPM provides real-time visibility across AWS, Azure, and GCP and automatically flags security risks before they become incidents.
3️⃣ How does CSPM detect cloud misconfigurations?
CSPM connects to cloud providers via secure, read-only APIs and continuously scans:
- IAM permissions
- Storage access settings
- Network exposure rules
- Encryption configurations
- Logging and monitoring setups
It compares these configurations against predefined security frameworks like CIS Benchmarks and alerts teams if something deviates from best practices.
4️⃣ What is the difference between CSPM and traditional security tools?
Traditional security tools focus on application vulnerabilities, malware detection, and network threats.
CSPM, on the other hand, focuses specifically on cloud infrastructure configurations. It prevents breaches caused by incorrect cloud settings rather than reacting to attacks after they happen.
- In simple terms:
- Traditional security reacts.
- CSPM prevents.
5️⃣ Can CSPM help with regulatory compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS)?
Yes. CSPM tools continuously monitor cloud environments against compliance standards such as:
- GDPR
- HIPAA
- PCI DSS
- SOC 2
- ISO 27001
They provide automated compliance scoring, policy enforcement, and audit-ready reports—reducing manual effort and improving audit readiness.
7️⃣ Is CSPM enough for complete cloud security?
CSPM is foundational but not complete on its own.
It focuses on configuration security. For full cloud protection, organizations often combine CSPM with:
- CWPP (Cloud Workload Protection Platform)
- CIEM (Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management)
- IaC scanning tools
Together, these form a Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) strategy that secures infrastructure, workloads, identities, and code.
6️⃣ Does CSPM support multi-cloud environments?
Modern CSPM solutions are designed for multi-cloud environments.
They provide unified visibility across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, helping organizations maintain consistent security policies and detect risks from a single dashboard.
This is especially important as businesses increasingly adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies.





